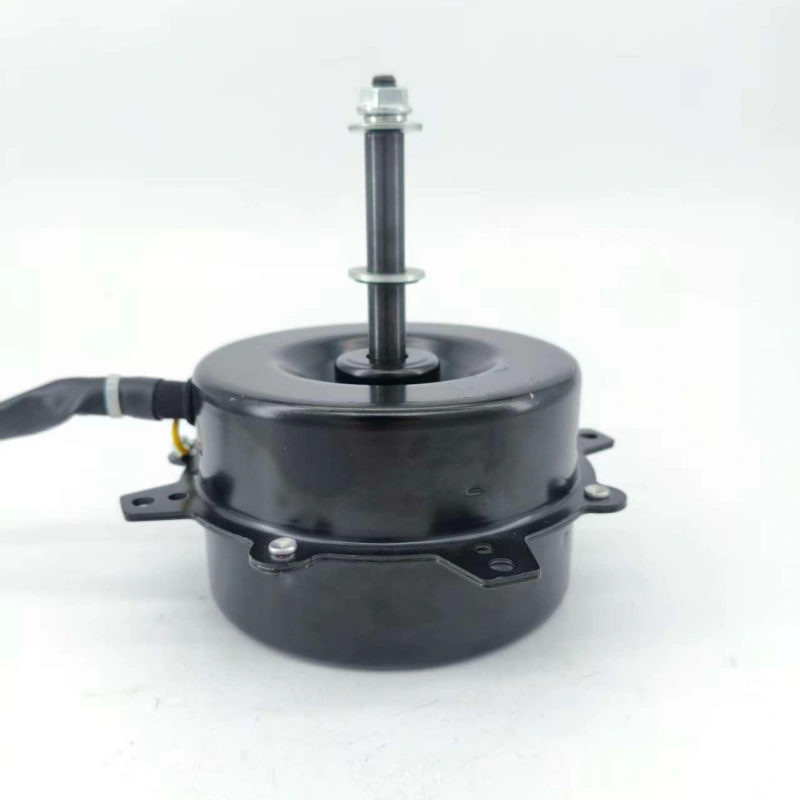
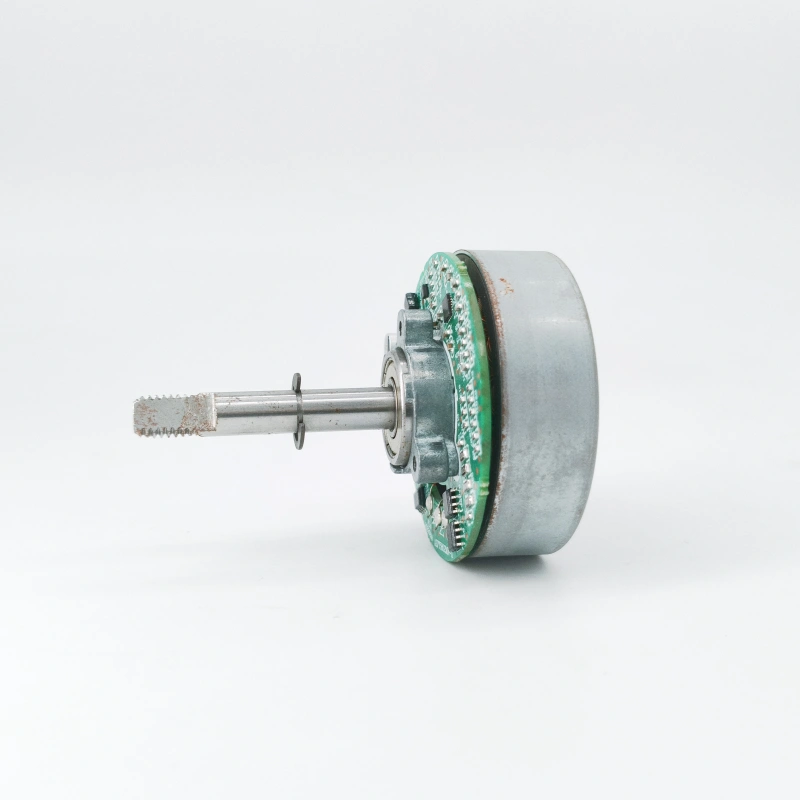
As the core power component of the equipment, the operating status of a water-cooled fan motor directly determines the cooling efficiency and service life of the water-cooled fan. Neglecting maintenance for a long time will lead to a series of problems: On one hand, the motor will accumulate dust, lint and other debris during operation. These impurities adhere to the motor windings and heat dissipation components, which will block heat dissipation, cause the motor temperature to rise too high. This not only reduces the cooling effect, but also may burn the winding coils and cause the motor to be scrapped. On the other hand, the working environment of the water-cooled fan has high humidity. If the bearings inside the motor lack lubrication or the seals are aging, water vapor can easily seep in, causing the bearings to rust and get stuck, increasing the operating noise of the motor, and even causing the motor to seize and fail to start, which seriously affects the normal use of the equipment. Therefore, regular maintenance is the key to ensuring the stable operation of the water-cooled fan motor and extending the service life of the equipment.
The specific maintenance methods can be divided into the following steps:
- Power-off Cleaning: Before maintenance, turn off the power supply of the water-cooled fan to avoid the risk of electric shock. Open the equipment shell, and gently clean the dust and debris on the motor surface and heat dissipation holes with a soft brush or the cold air gear of a hair dryer. Focus on cleaning the deposits in the gaps of the motor windings to ensure that the heat dissipation channels are unobstructed. If there is oil stain on the motor surface, wipe it with a cloth dipped in neutral detergent, and avoid using corrosive liquids that may damage the motor components.
- Bearing Lubrication: The motor bearings are wearable components, and their lubrication status needs to be checked regularly. Open the bearing end caps at both ends of the motor, and observe whether the bearing surface is dry and rusty. If the grease has dried up or deteriorated, wipe it clean with a clean cotton cloth, and then apply an appropriate amount of special motor grease (such as lithium-based grease). Note that the amount should not be too much, just enough to cover the bearing balls, to prevent the grease from overflowing and absorbing dust.
- Seal Inspection: Check whether the sealing strips and sealing rings at the connection between the motor and the water-cooling system are aging or damaged. If the seals are found to lose elasticity or have cracks, replace them in time to prevent the cooling water from leaking into the motor interior, which may cause short circuit or component rust. At the same time, check whether the insulation covering of the motor terminal is intact. If it is damaged, re-wrap it with insulating tape to prevent electric leakage.
- Operation Test: After the maintenance is completed, close the equipment shell, connect the power supply and conduct a trial operation. Observe whether there is abnormal noise or vibration when the motor is running, touch the motor shell with your hand to feel the temperature (the normal temperature of the shell should not exceed 60℃), and at the same time check whether the air volume and cooling effect of the water-cooled fan are normal. If any abnormality is found, stop the machine in time for inspection, and put it into use only after ensuring that the motor has no faults.
It is recommended to carry out basic cleaning and maintenance once a month, and a comprehensive inspection (including bearing lubrication and seal inspection) once a quarter. This can effectively reduce motor failures and extend the service life of the water-cooled fan.