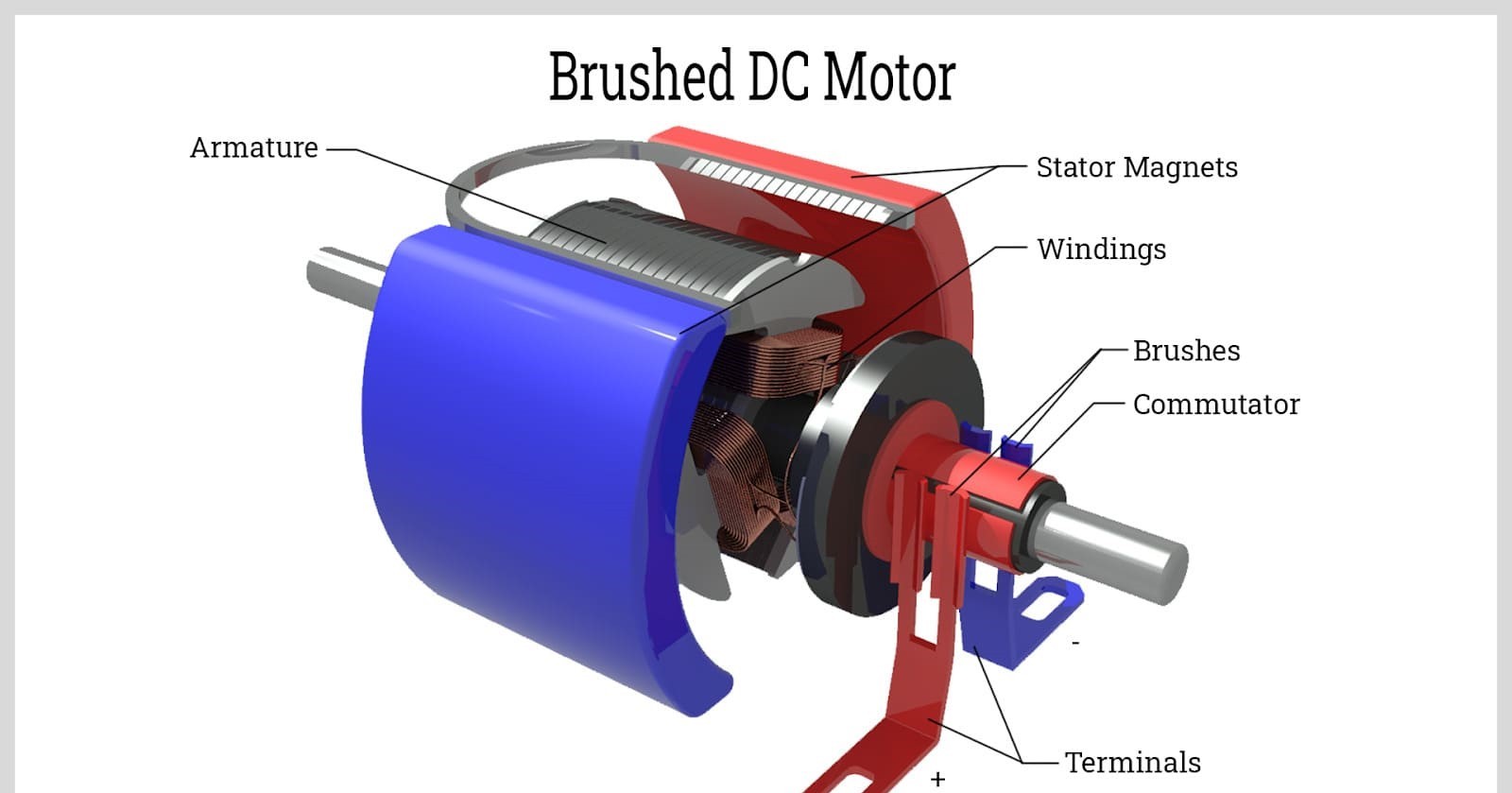
The three main types of DC motors are classified based on their excitation method (i.e. the generation of stator magnetic field), namely: separately excited DC motor, parallel excited DC motor, and series excited DC motor.
They have significant differences in structure, characteristics, and application scenarios, as follows:
1. Separate Excited DC Motor
core principle
The excitation winding of the stator (the coil that generates the magnetic field) is powered by an independent DC power source, which is different from the armature winding of the rotor (the coil that generates electromagnetic torque).
The circuits of the two are separated from each other and do not interfere with each other.
Key Features
High control accuracy: The excitation current and armature current can be independently adjusted, so the control of speed and torque is very precise.
Wide speed range: By adjusting the excitation current, a wide range of speed regulation can be achieved above or below the rated speed.
High cost: Due to the need for additional independent excitation power supply, the initial equipment cost and circuit complexity are higher.
Typical Applications
Suitable for scenarios that require high control accuracy, such as:
Industrial machine tools (lathes, milling machines, etc.)
Robot servo system
Traction Control of Electric Vehicles
2. Shunt Wound DC Motor
core principle
The excitation winding of the stator is connected in parallel with the armature winding of the rotor, and they share the same DC power supply.
The resistance of the excitation winding is high, so the excitation current flowing through is small and stable.
Key Features
Stable speed: When the load changes, the speed fluctuation is minimal and remains almost constant (because the excitation current is not affected by the load, the magnetic field strength is stable).
Moderate torque: The starting torque is moderate, suitable for equipment running smoothly, and not suitable for heavy load starting.
Simple structure: No need for independent excitation power supply, easy maintenance, and lower cost than other excitation motors.
Typical Applications
Suitable for devices that require stable rotational speed, such as:
Centrifugal water pump, ventilation fan
Conveyor belt, compressor
Printing machines, textile machinery
3. Series Won DC Motor
core principle
The excitation winding of the stator is connected in series with the armature winding of the rotor, and the same current flows through both the excitation winding and the armature winding, so the magnetic field strength is proportional to the armature current.
Key Features
Extremely high starting torque: When starting, the armature current is at its maximum and the magnetic field is the strongest, which can generate a starting torque far exceeding that of other types of DC motors.
The speed changes dramatically with the load: when the load is reduced, the speed will increase sharply (and may even damage the motor due to “flying”);
When the load increases, the speed significantly decreases.
Sturdy structure: The excitation winding has low resistance, few turns, simple and durable structure, suitable for harsh working conditions.
Typical Applications
Suitable for heavy-duty equipment that requires excessive starting torque, such as:
Electric locomotives, trams
Crane, winch
Internal combustion engine starter motor (such as car starter motor)