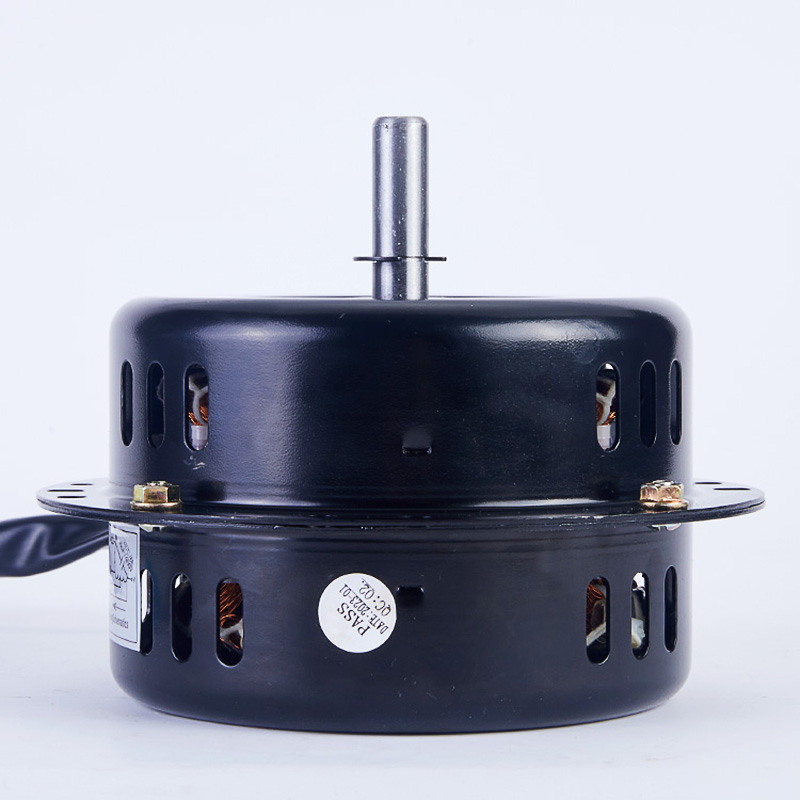
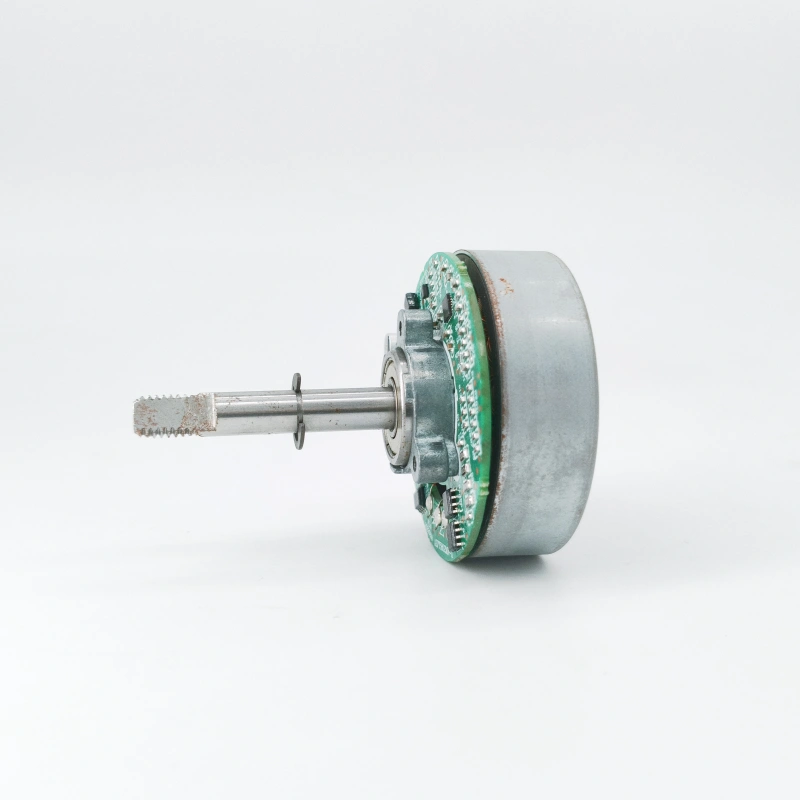
The core components of an AC motor are the stator and rotor, which convert energy through electromagnetic induction. They are then combined with auxiliary components such as bearings and end caps to ensure stable operation. The functional division of each component is clear.
1、 Core functional components (energy conversion core)
Stator (stationary part)
Core composition: composed of stator core, stator winding (coil), and machine base.
Core function: When AC power is applied, the stator winding generates a rotating magnetic field, providing the “power source” of electromagnetic force for the rotor and serving as the input end of electromagnetic energy for the motor.
Auxiliary function: The stator core is made of stacked silicon steel sheets, which can reduce hysteresis loss and eddy current loss, and reduce motor heating;
The base fixes the iron core and supports the entire motor structure.
Rotor (rotating part)
Core components: divided into squirrel cage rotor (cast aluminum conductor+end ring) and wound rotor (winding+slip ring), both equipped with rotor core.
Core function: Under the action of the rotating magnetic field of the stator, the rotor bars or windings will induce current, thereby generating electromagnetic torque, driving the rotor to rotate, and ultimately converting electromagnetic energy into mechanical energy (such as driving loads such as fans and water pumps).
Differential features: The squirrel cage rotor has a simple structure, low cost, and is suitable for ordinary scenarios;
The wound rotor can adjust the speed through external resistance and is suitable for working conditions that require speed regulation, such as cranes.
2、 Auxiliary support components (key to stable operation)
bearing
Installation position: located between the rotor shaft and the end cover.
Core function: Reduce the frictional resistance during rotor rotation, ensure rotor coaxiality, reduce wear and energy consumption, and directly affect the operating noise and service life of the motor.
end cover
Installation position: At both ends of the motor, fixed to the machine base.
Core function: Seal the interior of the motor to prevent dust and moisture from entering;
Simultaneously supporting the bearings, fixing the axial position of the rotor, and ensuring uniform “air gap” between the stator and rotor (uneven air gap can cause motor vibration and efficiency reduction).
Fan and heat dissipation structure
Common form: Install a fan at the end of the rotor shaft, and match it with the heat sink or ventilation hole on the machine base.
Core function: During the operation of the motor, heat is generated due to copper and iron losses. The fan rotates to drive the airflow and expel the heat from the outside of the motor, preventing the winding from overheating and burning out, and maintaining the motor operating within a safe temperature range.
junction box
Installation position: outside the machine base.
Core function: As an external interface for the stator winding, it facilitates the connection of power and control lines, while insulating and protecting the wiring terminals to prevent the risk of electric shock or short circuit.