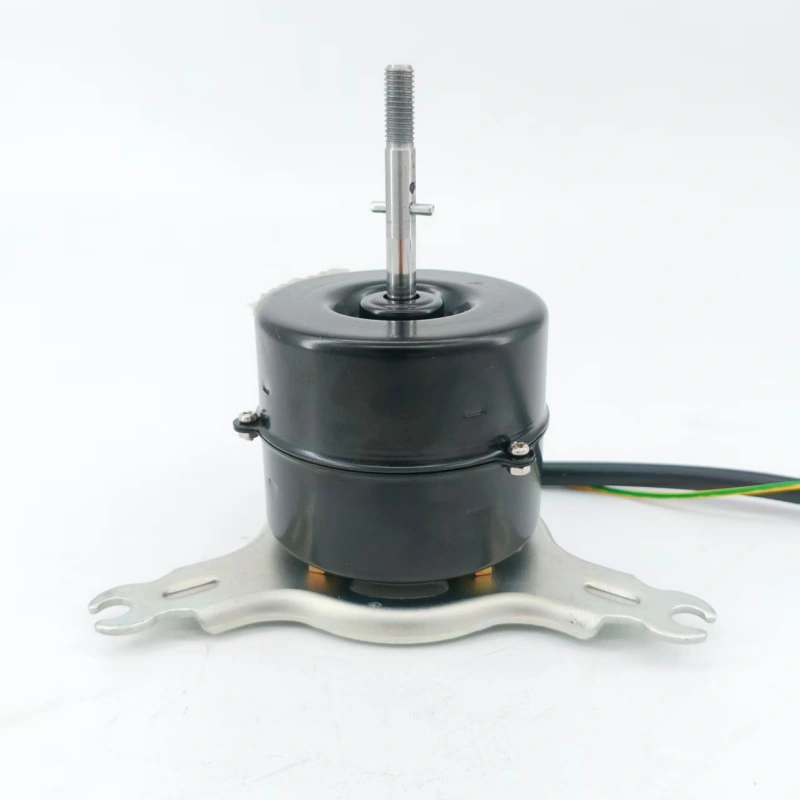
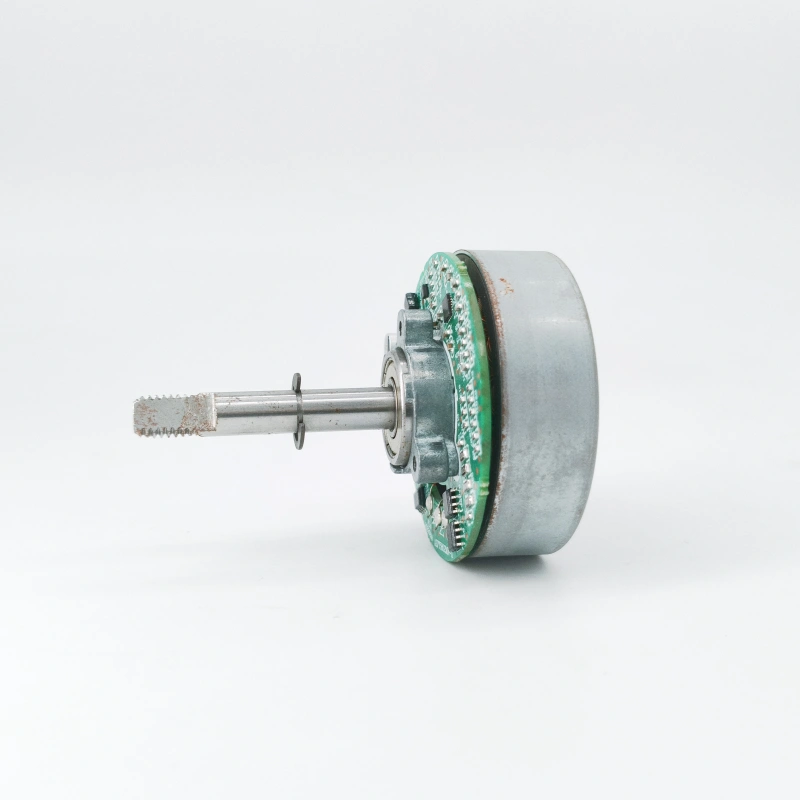
DC motors are widely used in machine tools, electric vehicles, precision instruments and other fields due to their excellent speed regulation performance and large starting torque. Rotational speed stability is one of their core performance indicators. The essence of unstable rotational speed lies in the imbalance between the output torque of the motor and the load torque, or abnormal signal transmission in the speed regulation system. Specifically, the causes can be traced from three aspects: mechanical structure, electrical system and control module, and targeted solutions can be implemented accordingly.
1. Abnormal Mechanical Structure: Physical Obstacles to Torque Transmission
Wear or assembly deviation of mechanical components will directly damage the stability of the motor’s power transmission. First of all, bearing failure is a common inducement. Lack of oil in bearings, wear of balls or breakage of retainers caused by long-term operation will make the rotational resistance of the rotor fluctuate, leading to fluctuations in rotational speed. Secondly, improper installation of the coupling, such as misalignment of the axis and aging of elastic parts, will cause impact in power transmission and result in instantaneous changes in the motor load. In addition, the slack or slippage of the transmission belt connecting the motor and the load, as well as the jamming at the load end (such as the unsmooth movement caused by the wear of the machine tool guide rail), will make the actual load of the motor deviate from the rated value, thereby leading to abnormal rotational speed.
The solution to such problems should focus on “restoring the precision of mechanical fit”: regularly lubricate and maintain the bearings, use special grease and check the wear condition, and replace them in time when the wear exceeds the standard; recalibrate the coupling axis, replace the aging elastic components, and ensure that the coaxiality error is controlled within 0.1mm; adjust the tension of the transmission belt, remove foreign objects at the load end and overhaul the moving components to ensure the stable operation of the load.
2. Electrical System Failure: The Root Cause of Unstable Energy Supply
The electrical system is the power source of the motor, and its failure will directly lead to fluctuations in input energy. First, power supply problems: if the filter capacitor of the DC power supply after AC rectification fails or one arm of the rectifier bridge is damaged, the input DC voltage will contain a large number of ripples, resulting in unstable armature current. Second, armature winding failures: inter-turn short circuit of the winding, loose wiring or oxidation of the commutator segments will cause the armature circuit resistance to fluctuate, affecting the output of electromagnetic torque. Third, abnormal excitation system: open circuit or poor contact of the excitation winding of the separately excited DC motor, or sudden changes in the excitation circuit resistance of the shunt-excited motor, will lead to changes in the main magnetic flux. According to the rotational speed formula n=(U-IaRa)/(CeΦ), the fluctuation of magnetic flux Φ will directly cause violent changes in rotational speed.
The solution to electrical failures relies on “accurate detection + targeted repair”: use a multimeter to detect the ripple coefficient of the power output voltage, replace the failed filter capacitor and damaged rectifier components, and ensure the DC